The Urgent Need for Hypervisor Security in Healthcare
In today’s digitized healthcare landscape, virtualization technology allows healthcare organizations to consolidate infrastructure, streamline IT management, strengthen security and regulatory compliance, and ultimately improve patient care. However, it also expands the attack surface. Healthcare providers rely on virtualized environments to manage sensitive patient data. As a result, hypervisors have become a prime target.
Hypervisors underpin essential healthcare systems. These include EHRs, telemedicine platforms, medical imaging, and IoT device management. As the layer responsible for managing virtual machines (VMs), hypervisors are uniquely positioned to control the systems that sustain patient care. Yet many healthcare hypervisors remain underprotected. That makes them high-value targets for ransomware groups like BlackCat. Safeguarding hypervisors is a cybersecurity priority. It is also essential for patient safety and continuity of care.
Why the healthcare sector?
Healthcare organizations handle highly sensitive data, a blaring factor in their attractiveness to cybercriminals. After gaining access to an exposed hypervisor, threat actors can easily take down the entire virtualized environment of a hospital by spreading ransomware to all managed VMs containing sensitive data. Beyond data sensitivity, attackers expect high payouts. Recent studies suggest that expectation drives targeting. In a 2024 survey of 402 healthcare institutions, 53% paid ransoms with an average of $4.4 million. When lives are at stake, hospitals face a terrible choice. They can pay or risk downtime and disruption. This dilemma has unfortunately likely contributed to making them a reliable target for threat actors.
Moreover, many healthcare facilities have limited resources for cybersecurity. As a result, hypervisors often receive less protection. Without specialized security operations centers, many IT departments handle both operations and cybersecurity, leaving systems especially vulnerable. According to a 2024 report, 52% of healthcare respondents expressed significant concern about cybersecurity vulnerabilities stemming from employee error alone. Gaps in resources and training leave virtualized systems exposed. Limited hypervisor protections widen that risk.
The scope
The prevalence of ransomware attacks in healthcare is staggering. As of 2024, healthcare institutions experienced about 2,000 attacks per week, 15% higher than last year’s findings. This places the sector in the top three most targeted industries worldwide. In addition, 92% of organizations reported experiencing a cyberattack in 2024, up from 88% the previous year. This surge in attacks draws attention to the vulnerabilities within the healthcare sector, with recent incidents exposing the far-reaching impacts on patient data.
In February of 2024, Change Healthcare faced one of the largest cyberattacks in U.S. healthcare history. The attack was attributed to BlackCat, which is known for targeting ESXi and virtualized environments. It exposed sensitive data from over 100 million individuals. The impact reached nearly a third of the nation’s healthcare interactions. This incident broadcasted the severe vulnerability of healthcare institutions, and the risks cyberattacks pose, from disruptions in pharmacy and claims processing to delays in medical services.
The financial and operational fallout from incidents like these is profound.
Healthcare remains the most expensive industry in incident response, with an average of $9.8 million in 2024. Downtime adds a significant portion to this, with many healthcare organizations reporting that it took over a month to recover from an attack, showcasing the protracted disruption that ransomware inflicts on healthcare delivery. Over the past four years, downtime has cost healthcare providers approximately $900,000 per day, with an estimated $10 billion in cumulative losses tied to ransomware incidents alone. Yet, the most severe impact of these breaches is felt in nearby facilities and in the quality of individual patient care.
When ransomware paralyzes a facility’s virtual infrastructure, patients seek care elsewhere. Neighboring hospitals absorb the surge. Care quality can decline for everyone. A recent study examined the effects of ransomware on healthcare systems and reported the dire consequences of how these attacks cascade through the broader healthcare network. In this study, stroke activations surged by nearly 75%, while confirmed stroke cases more than doubled. Cardiac arrest incidents rose by 81%, yet the survival rate for out-of-hospital cardiac arrests plummeted from 40% pre-ransomware attack to just 4.5%. Unaffected hospitals faced prolonged wait times, higher numbers of patients leaving without being seen, and longer stays. The threat of hypervisor ransomware in healthcare is evidently more than technical—it’s a real threat to life.
Next steps
These scenarios, coupled with the historical lack of protection for hypervisors, emphasize the urgent need for a hypervisor ransomware protection strategy across the healthcare sector. Hypervisor attacks in healthcare do more than compromise patient information; they disrupt critical care, delay treatment, and can put lives at risk. The path forward demands a shift in mindset. Healthcare providers must prioritize hypervisor security as a core component of patient care. By adopting a robust, multi-layered security framework that integrates advanced AI detection, endpoint protection, and system-wide encryption, healthcare institutions can better protect their virtualized environments—and the lives that rely on them.
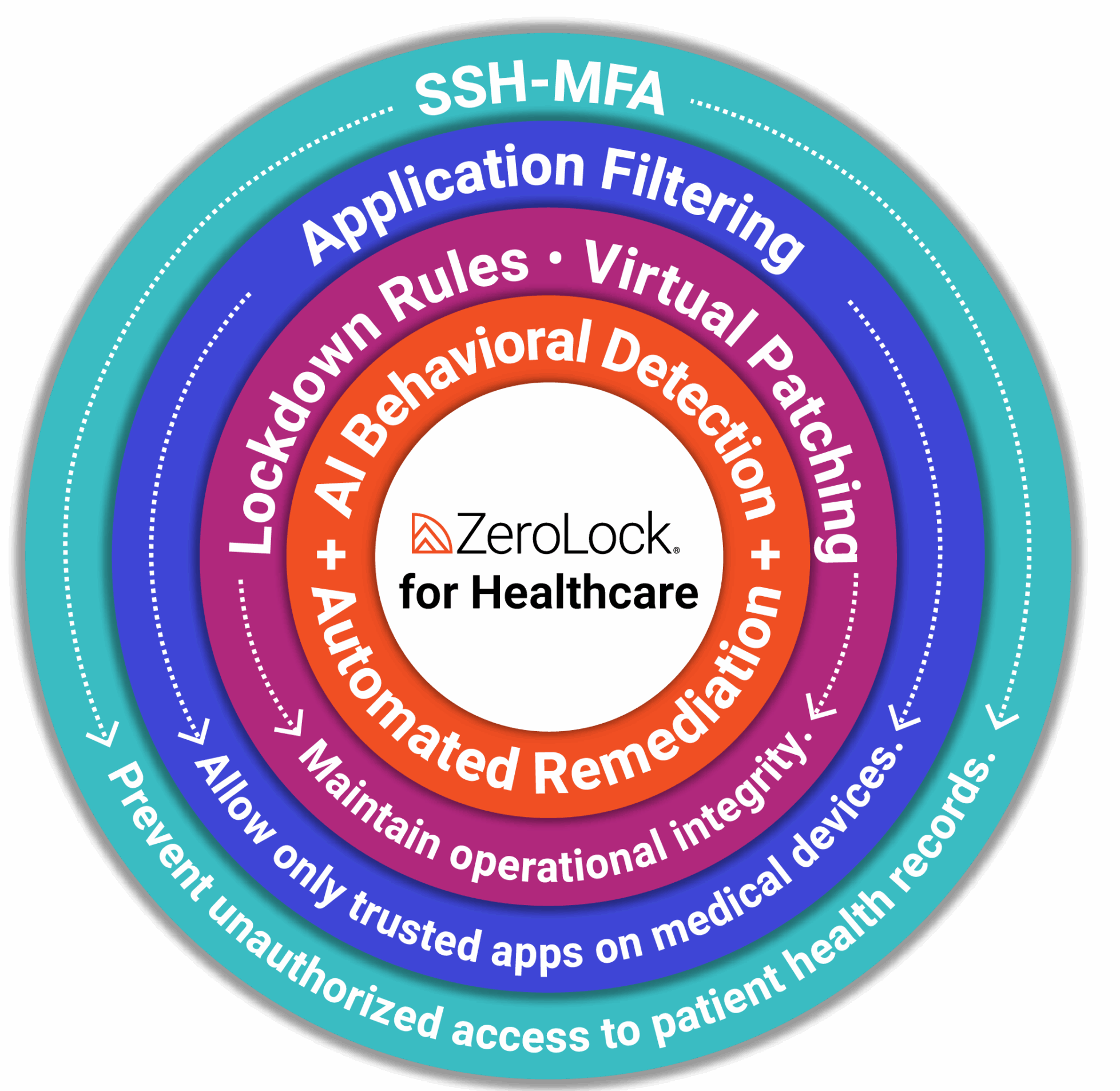
Solutions like ZeroLock, which is designed to provide deep protection for hypervisors and virtual environments, offer healthcare organizations tools to monitor and respond to threats before they escalate. ZeroLock’s features, including AI detection, ransomware detection, automated rollback capabilities, and virtual patching, address these challenges head-on. This approach helps healthcare providers ensure that critical systems remain operational and that patient data stays secure.
A proactive approach to hypervisor security goes beyond protecting data; it’s about preserving patient safety and maintaining trust in an era where health and technology are inextricably linked. By adopting dedicated tools to defend hypervisors, healthcare organizations can take decisive steps to reduce cyber risks, safeguard patient care, and strengthen the integrity of healthcare as it becomes increasingly reliant on virtual infrastructure.
